Oral Biopsy (Hard and Soft Tissue)
Accurate Diagnosis for Hard and Soft Tissue Lesions
When Is an Oral Biopsy Needed?
An oral biopsy is a diagnostic dental procedure in which a small sample of tissue from the mouth or jaw is removed and examined in a laboratory. Dentists use oral biopsies to identify abnormal or suspicious areas and provide an accurate diagnosis.
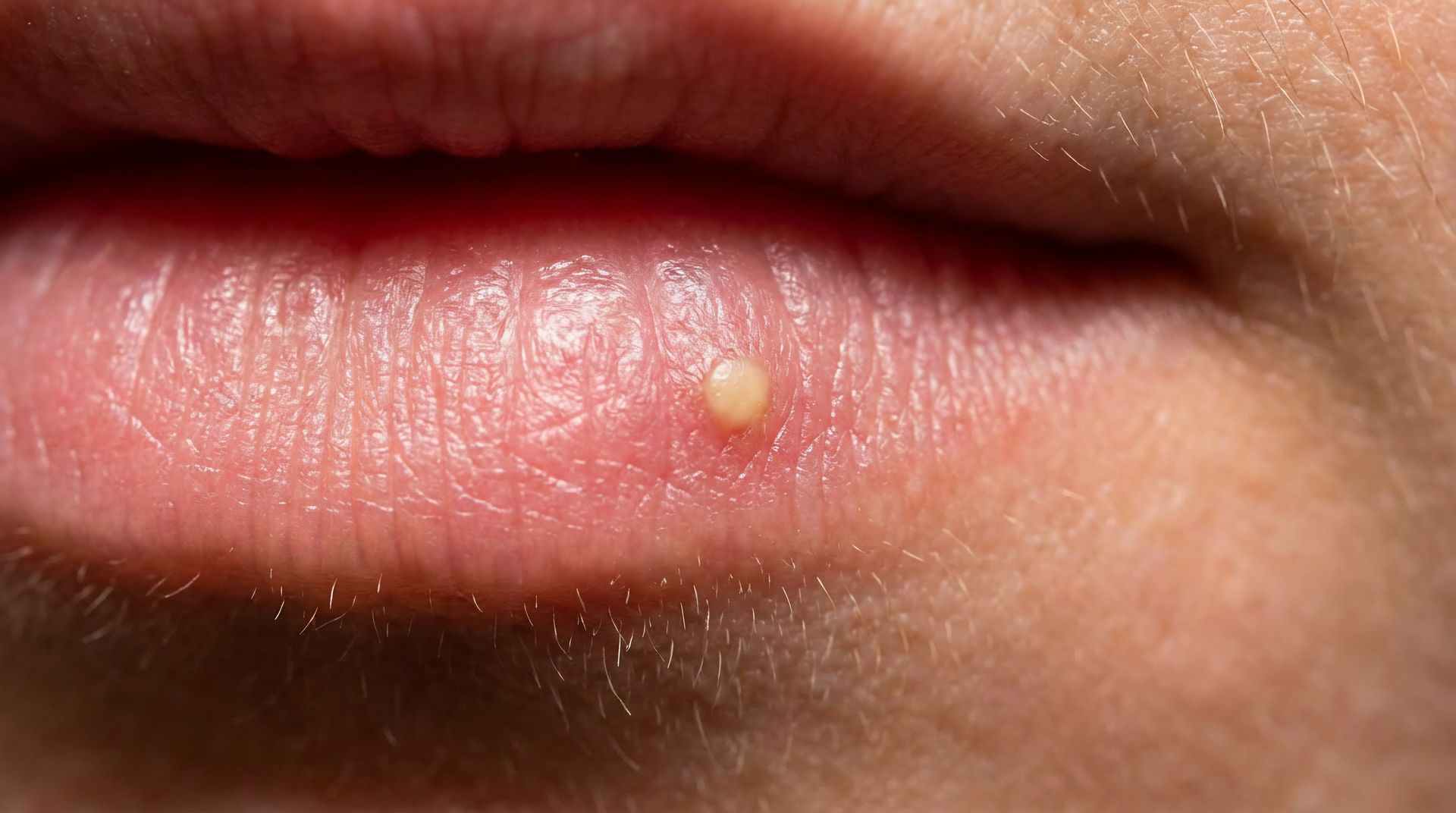
A sore or ulcer that does not heal
Red or white patches in the mouth
Lumps, swelling, or thickened tissue
Unexplained pain or bleeding
Abnormal findings on dental X-rays involving the jawbone
Types of Oral Biopsy
Our periodontal cleanings are performed with precision, comfort, and a patient-centered approach. Your visit is designed to gently remove disease-causing bacteria and support long-term gum stability.
Soft Tissue Oral Biopsy
A soft tissue biopsy involves removing a small sample from the oral mucosa, including the gums, tongue, cheeks, lips, or palate. This type of biopsy is commonly used to evaluate:
- Non-healing ulcers
- Oral lesions or growths
- Suspicious color or texture changes
- Possible oral cancer or precancerous conditions
Hard Tissue Oral Biopsy
A hard tissue biopsy involves sampling bone or tooth-related structures, usually from the jaw. This type of biopsy may be recommended when imaging studies reveal:
- Jawbone lesions or cysts
- Abnormal bone growth or destruction
- Lesions around impacted teeth
- Changes near dental implants
- Suspected tumors of the jaw
FAQs about Oral Biopsies
How Is an Oral Biopsy Performed?
Most oral biopsies are performed in the dental office or surgical setting under local anesthesia. Hard tissue biopsies may occasionally require sedation. The procedure is generally quick, and dissolvable stitches may be placed to aid healing.
Is an Oral Biopsy Safe?
Yes. Oral biopsies, both hard and soft tissue, are safe procedures. Temporary swelling, mild discomfort, or minor bleeding may occur, but serious complications are rare. Your dentist will provide post-procedure care instructions to promote healing.
When Will Results Be Available?
Biopsy samples are sent to a specialized oral pathology laboratory. Results are typically available within 10-14 days, after which your dentist will review the findings and discuss any necessary treatment or follow-up.
Importance of Oral Biopsies
Early diagnosis of oral conditions, including oral cancer and jawbone diseases, significantly improves treatment outcomes. Hard and soft tissue oral biopsies play a critical role in maintaining oral and overall health.